Like my previous guide to SEO for BigCommerce, this post provides a comprehensive guide to Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) for Shopify. Covering all aspects from optimising product pages and collections to improving website speed and technical SEO.
It highlights the importance of using relevant keywords, structuring content correctly, and building high-quality backlinks.
The post also suggests ways to improve user experience and conversion rates, such as optimising page load times and implementing clear and concise call-to-actions.
Overall, the guide serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to improve their Shopify store’s visibility and ranking on search engines.
An Introduction to Shopify
Shopify is a cloud-based eCommerce platform that is designed for easy setup and primarily caters to small businesses.
Originally conceptualised in 2006 by Tobias Lütke, Daniel Weinand, and Scott Lake a group of individuals who were dissatisfied with the available eCommerce solutions at the time. Shopify has grown to become the go-to resource for over 4 million active online shops (Source: Builtwith.com.).
If you are starting out in the eCommerce arena or running a small business, Shopify offers an uncomplicated solution that comes with built-in analytics, reporting and SEO capabilities, all accessible through a user-friendly admin system. Hosting costs are included within a small monthly fee, making Shopify an affordable option compared to renting a physical shop.
Over the last few years, Shopify has witnessed a staggering growth in its store numbers, increasing by more than 200% since 2020. The period between March 2020 and January 2022 saw a remarkable boost of 201.53% in Shopify’s store growth, which can be attributed to the over 2.5 million new stores that were launched within this period.
This increase is largely attributed to the COVID pandemic, which led to a massive shift of traditional brick-and-mortar retailers to online platforms like Shopify for their business operations. (Source: Genus AI.)
Shopify is used by merchants in over 175 countries around the world, with the second largest market being the UK, where, according to Builtwith.com there are 178,882 live sites.
The significance of these statistics lies in the fact that selecting a hosted solution for your online store requires placing immense trust in the provider company. Past instances, such as the shutdown of Magento Go, posed severe challenges for its users who had to migrate their stores to a new platform with limited time.
Nonetheless, Shopify boasts an extensive user base and market share, reducing the chances of a similar situation. This indicates that Shopify is a reliable platform, and the likelihood of it shutting down abruptly is highly improbable.
Is Shopify Good for SEO?
In the most part Shopify is good for SEO and all the basics are well covered, it has multiple built in features & apps that are designed to effectively assist in getting your website pages indexed and ranking in search engines. Shopify is considered by many to be the most easy ecommerce platform for SEO.
As with all platforms it does have its limitations but the benefits do tend to outweigh these.
Generate XML Sitemap
XML sitemaps are designed to provide search engines with a better understanding of the structure behind your digital store. The intended result behind this is that the search engine bots can crawl and index your site with ease.
Shopify automatically generates an XML sitemap for your store at yoursitedomain/sitemap.xml
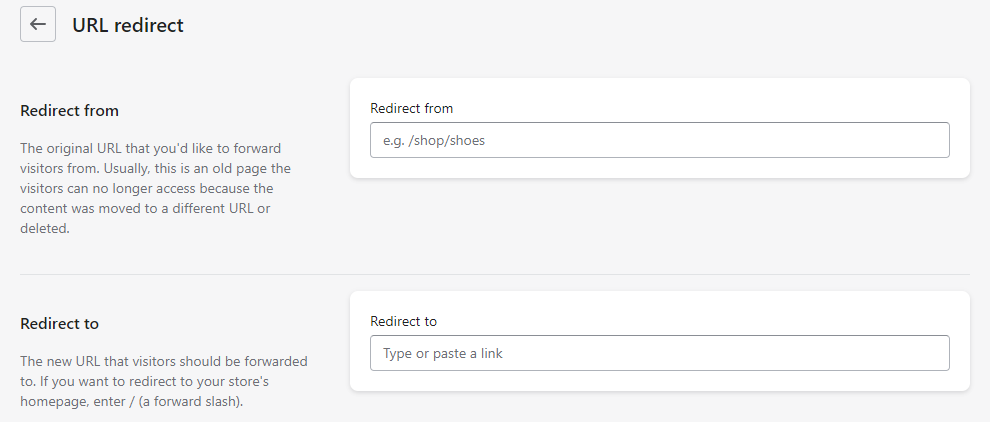
301 Redirects
Since making adjustments to a link will remove its name on search engines’ ranking. It is not recommended to change urls especially if they have earned traction and ranking within the search engines.
However, this is sometimes unavoidable and we may need to implement redirects in order to resolve a situation. This is another useful feature available to users out of the box with Shopify.
Global redirection
The presence or absence of “www” in a website’s URL is typically inconsequential to most users. However, it can significantly impact a website’s search engine ranking if the website is accessible through both versions of the URL.
This creates internal duplicate content, which can confuse Googlebot and make it more difficult to accurately index the most relevant page for a given search query. Moreover, Google may interpret links pointing to both versions of the URL as separate pages, resulting in a distribution of link power between the two domains.
As a result, both domains may rank lower than if the link power were consolidated on a single version of the website.
Aside from its implications for search engine optimization, selecting a preferred domain (www or non-www) is also a critical component of a website’s technical setup and is therefore essential for all webmasters to address.
In Shopify the solution for this is implemented via Online Store > Domains > Change primary domain
Robots.txt
A well implemented robots.txt file is a way of informing the search engines which pages of the website we want them to crawl and those we do not. Ranking well on search engines means ensuring that every link that we want indexed is valuable and unique and if they aren’t we don’t want them indexed.
All websites inherently have pages and areas of the site that are not valuable to the search engines and as such shouldn’t be indexed. These include things such as admin and checkout pages or internal search pages among others.
Shopify automatically generates a default robots.txt so newcomers to SEO don’t need to worry about its existence and Shopify states that the default file works well for most stores.
You can check the robots.txt file at domain.com/robots.txt
As your Shopify store grows there may be a need to edit the default file and up until June 2021 this was always an issue as there was no access provided in order to do this. Shopify now let you update the robots.txt file but it does come with a cautionary warning.
The following changes can be made:
- Allow or disallow certain URLs from being crawled.
- Add crawl-delay rules for certain crawlers.
- Add extra sitemap URLs.
- Block certain crawlers.
If however, you understand code and would like to edit the file this is where you need to go in your Shopify account.
- Login to your Shopify admin area
- In the left sidebar, go to Online Store > Themes
- Choose Actions > Edit code
- In “Templates”, select the “Add a new template” link
- Find the left-most dropdown and choose “robots.txt”
- Choose “Create template”
This will make the template for the default robots.txt file visible and editable, the code isn’t too difficult to add and there is some great advice in the official documentation from Shopify and following this guide should allow owners to have much more control over the Shopify site and which URLs can be crawled.
Mobile-friendly stores
Most webmasters and SEOs agree that these days mobile commerce is the dominant area for most shopping platforms with more and more people making purchases directly from smartphones.
According to forecasts, retail sales from m-commerce in the UK are expected to surpass the 100 billion British pounds mark by 2024 (Statista.com)
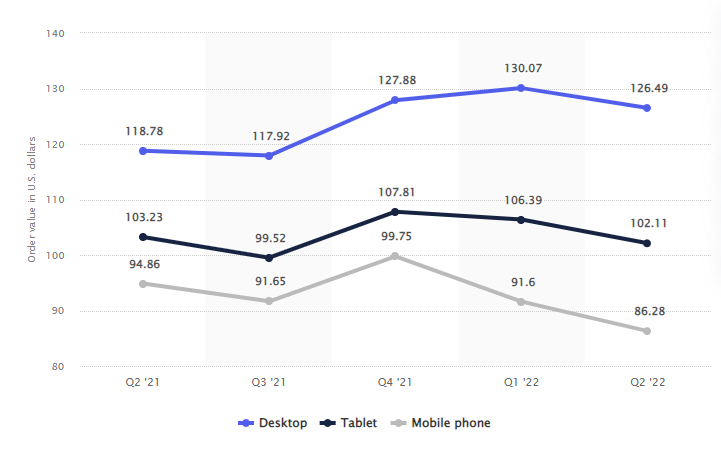
Average value of online shopping orders in Great Britain from 2nd quarter 2021 to 2nd quarter 2022, by device (Statista.com)
Most websites these days come under Mobile First Index so the more mobile friendly your store is the more likely it is to rank well in search engines.
As a platform Shopify provides its users with an ample supply of mobile friendly, responsive design themes enabling your store to look fabulous as well running smoothly on all devices and improving your SEO.
Site Speed
It is said that Google when ranking search results prioritises speed, giving sites that have fast load times an advantage over those that take longer. This has been a known ranking factor with Google as far back as 2010.
An April 2010 announcement confirms Google’s search algorithm would start taking speed into account when ranking search results:
“Like us, our users place a lot of value in speed – that’s why we’ve decided to take site speed into account in our search rankings.”
For a long time Shopify have been working to make stores on their platform fast by default, utilising CDN and a faster global network, they also optimise all images to Webp (image format 30% smaller than jpeg with similar quality making for a lighter site) automatically.
Shopify is really well known for its speed, most other platforms require store owners to have their own server, Shopify does not.
GA Integration
An important aspect of growing your business website is understanding your visitor data in order to identify what is going on with your website. There are any number of tools that can be used to collect this data but the most popular by far is Google Analytics.
At the time of writing Universal Analytics is fast approaching its sunset and Google have stated that on July 1st 2023 standard Universal Analytics properties will stop processing data so we strongly encourage you to make the switch to GA4 as soon as possible if you haven’t already.
Shopify has been a bit slow out of the box on this one and although there have been some workarounds for some time they have now implemented GA4 out of the box.
Shopify has a really good post on Implementing GA4 so I won’t cover that aspect in this post I will just leave you with a link to the article.
Canonicalization
Introduced in 2009 by the major search engines the canonical tag is a means for webmasters to solve duplicate content issues whilst preserving link equity and rankings.
The tag itself is a snippet of html code that identifies a specific page as the main focus page where there are duplicates or pages of great similarity. If viewed in the website code it would appear like this: link rel = “canonical” href = “example.com”. “link rel” means this link is the master version of the page and “href = example.com” means the canonical version can be found at the specified url.
In simple terms without the use of canonicalization websites can end up with duplication issues and if these duplicate pages both get indexed then the search engines do not understand which page is the most important when it comes to ranking and can therefore lower both pages in the SERPs and thus water down your SEO efforts.
Shopify have endeavoured to resolve this issue straight from the start and pages and their canonical are set automatically.
On-Page SEO
When it comes to enhancing a website’s SEO, on-page SEO is the most familiar area to most people. This refers to the optimization of individual web pages to increase search engine rankings and attract relevant traffic. On-page SEO entails optimising content, images, and HTML source code.
These techniques include incorporating keywords in the page title, header tags, meta descriptions, and throughout the content. It also includes ensuring that the website provides a user-friendly experience.
On-page SEO covers a range of disciplines, including metadata optimisation, keyword research, and structured data or schema. In the following section, we will delve into some of these disciplines.
Keyword Research is Important
Keyword research is a crucial aspect of SEO as it helps understand the words and phrases that people use to search for a website’s products, services, or information. By identifying and utilising these keywords, a website’s content and meta tags can become more relevant to search engines, improving its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
It also allows businesses to understand their target audience better, enabling them to create more effective marketing strategies and attract qualified traffic to the website.
Tools such as Google AdWords Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, and SEMrush are used to complete keyword research. Filtering out irrelevant keywords is necessary as not all keywords generated by these tools will be relevant to a website’s business.
SEO professionals generally classify keywords into four categories: informational, navigational, transactional, and commercial. These types of keywords signal to search engines the searcher’s intent, indicating whether they desire information, are already knowledgeable about the business or product, or want to make a purchase.
Use keywords with both Commercial and Informational intent
There is a consensus among SEO experts that four keyword types exist, namely Informational, Navigational, Commercial, and Transactional. By identifying the intent type of a keyword, it is possible to infer whether a searcher is seeking to purchase something imminently, compare options, or gather information.
Informational: The terms used by individuals searching for information are called informational keywords. Although these keywords generally have high search volume, they do not always lead to conversions.
However, they are still valuable for generating brand awareness. These types of keywords often include question words such as “what is” and “how to,” and can lead to knowledge panels displayed by Google.
Navigational: Navigational keywords refer to search terms that are used to locate a particular website or webpage. Typically, these keywords are employed to locate a specific brand or company and contain the brand or company name in the query.
For instance, “Amazon” would be a navigational keyword for the Amazon.com website, while “BBC News” would be a navigational keyword for the BBC News website.
Unlike informational or transactional keywords, which are used to find information or facilitate a transaction, navigational keywords are used by individuals who are already familiar with the brand or product and wish to locate the correct website or physical location to access their offerings.
Transactional: Transactional keywords are search terms that demonstrate the intention to buy a product or service. These keywords often include words such as “buy,” “purchase,” “discount,” “coupon,” “order,” “shop,” and “prices.” They are used by consumers who are actively seeking to make a purchase, rather than just browsing or researching a product or service.
For instance, “buy new shoes online,” “discounted laptops,” and “coupon code for flower delivery” are all phrases that indicate transactional intent.
Optimising for transactional keywords can enhance sales and revenue for an e-commerce website, and help businesses reach potential customers who are actively seeking to make a purchase.
Commercial: During the consideration phase of the funnel, users rely on keywords that demonstrate commercial intent. These keywords indicate interest in a specific product or service and typically result in a purchase.
For example, the keyword phrase “best pushchair for twins” is an example of commercial intent. Individuals using this search query are likely parents with twins who require a pushchair and are searching for the best available options.
By identifying and using different keyword types, businesses can develop effective SEO strategies that attract valuable traffic, leading to increased sales and revenue.
Shopify and On-Page SEO
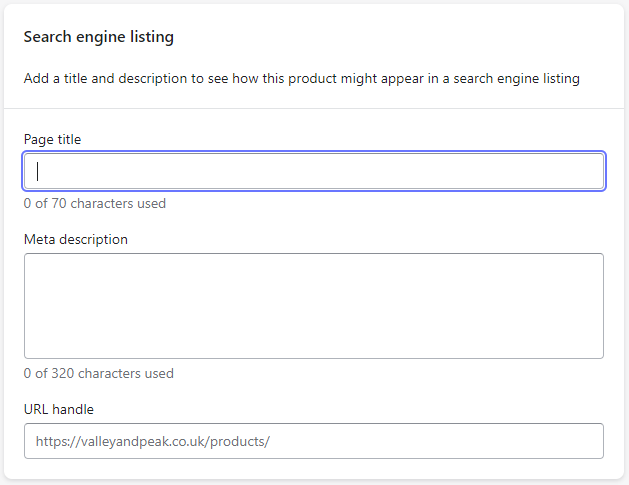
On-page SEO is relatively easy on Shopify once the relevant research is completed, Shopify will prompt you for this information whenever you add a new product.
Scroll down to the last section of the add product page and you will find the search engines listing preview as following:
As can be seen in the screenshots above Shopify does have character limits on the Title and the Meta Description, however, these are not the optimal numbers as recommended for SEO and can lead to confusion. While there is nothing wrong with the longer description it is likely to be truncated by Google so we would recommend sticking to the 160 characters if possible.
SSL Certificate
To keep user data secure, ensure website ownership, thwart attackers from creating fake versions of the site, and convey trust to users, a website necessitates an SSL Certificate.
For BigCommerce website owners, having an SSL certificate is necessary for an HTTPS web address. SSL certificates aid in securing information such as login credentials, bank account information, card transactions, personally identifiable information (name, address, D.O.B., telephone numbers), medical records, contracts, and legal documents.
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, a security protocol that establishes an encrypted connection between a web server and a web browser.
Shopify provides all websites on its platform with an SSL certificate by default. Simple and easy!
As you can see from all of the above Shopify performs SEO quite well straight out of the box, however, there are always ways you can improve and that’s what we will cover in the next section.
Site Structure and its Importance
Quite often overlooked, site structure is an important aspect of any SEO strategy and not only for Google indexing the site but for user experience (some would say more important).
Site structure when implemented correctly can improve user time on the site as well as allowing Google (other search engines are available) to index properly and thus provide pertinent information that is tailored to search needs and behaviour in order to determine site rank.
Search engines crawl websites from the top down so it is important to ensure that as many pages as possible are accessible within 2 to 3 clicks from the home page. If you bury pages or worse still have pages that are not linked in any way from other pages (orphaned) then the search engine bots will have a harder time finding and thus indexing those pages.
Shopify Specific
Regardless of theme all URLs on Shopify can be defined by three general structures:
Products – /products/example-product
Collections – /collections/collection-name (categories)
Pages – /pages/example-page (contact us, about us etc)
While this makes Shopify very easy when setting up as this will preserve the structure of URLs throughout the use of the domain it can bring with it limitations.
You cannot, for example, introduce sub-folders to a collection to facilitate a subset (sub-category) of products. So, no product types or brands as these would have to have their own collection.
X Tents/Two-Man
Shopify Product URL
Shopify’s default URL structure has some limitations, by default your product URLs are placed in a subdirectory under your Collections (Category Pages). This means if you have a product with the handle Hogwarts-Christmas-Mug and your Collection has the handle Mugs you will end up with a URL as seen below:
/collections/mugs/products/hogwarts-christmas-mug
Or at least this is how it would appear to be, when you take a closer look at the URL you will see that in reality the URL is:
/products/hogwarts-christmas-mug
While the collection version of the URL is making use of a canonical tag to the /products/product-name version (automatically created as mentioned earlier) this is not ideal for a number of reasons.
- Google sees canonicals as a recommendation only and can choose (and quite often do) to ignore them and as such could still index the collection version or worse both collection and product causing duplication.
- The majority of all internal links to products will then be canonical URLs which at best is a waste of crawl budget.
There is, however, a fix for this but once again you will be editing one of the liquid theme files, so unless you are competent within the code it is best to speak to a specialist. This could cause some issues with the breadcrumbs, so make sure that all links within the breadcrumbs are working after this change.
Firstly, in the Shopify CMS navigate to Online Store -> Themes -> Live Theme -> Actions -> Edit Code -> Snippets -> product-grid-item.liquid
Within the liquid code identify the following:
href=”{{ product.url | within: collection }}”
update the code to match the following:
href=”{{ product.url }}”
Have a quick scan through the code and ensure there are no other mentions as sometimes it is implemented in more than one place. Click save and it’s done. When editing any code we always recommend taking a copy of it first so you can replace it quickly if any issues arise.
Adding Noindex, nofollow
While these two words sound like gobbledegook to most, SEOs and Webmasters understand they can be powerful tools in optimising your site.
As its name suggests the Noindex tag is a way of preventing search engines from indexing any given page and while this may seem counterintuitive to what we are discussing, preventing certain pages from appearing in the SERPs can be integral to your SEO strategy.
A good example of a page you don’t want indexing would be a thankyou page that is the result of some lead gen that is offering something as a download, wouldn’t get many leads if that page was readily accessible from the search engine.
To control these pages and what appears in the search engine indices Shopify allows both these tags to be applied. It can be applied in a number of methods, added to the theme.liquid to control which pages are crawled and indexed at a page or via templates Hide a Page from Shopify
Like the Noindex tag the nofollow tag prevents the search engines from crawling any links on a page and thus prevent any link juice or ranking signals to be passed to the linked page.
Nofollow can be included using the same method, however, by including “nofollow” instead or, or as well as nofollow (for example noindex, nofollow).
Structured Data
In 2011, the major search engines collaborated on a standard initiative known as Schema, which established a common language and shared vocabulary for representing data. This language, also known as structured data, enables the organisation of content on webpages in a way that facilitates discovery and comprehension by search engines.
There are numerous types of Schema Markup available, with Google currently recognising 32 different types, ranging from Article to Video. In this article, we will focus on Product schema, a type of structured data markup that can be applied to web pages to provide search engines with information about products, including pricing, availability, and reviews.
Search engines can use this information to display rich snippets in search results, enhancing the webpage’s visibility and click-through rate. Additionally, other platforms, such as Google Shopping, can utilise product schema to present product information in a more visually appealing and user-friendly format.
Shopify itself doesn’t provide facility for adding structured data to your store, however, these days there are a significant number of Shopify Themes that do have this functionality built in.
If your theme doesn’t include structured data then don’t despair as there are still ways that you can add this useful element to your store. Before you implement any structured data there are a few things to consider.
- Define your main page types. For Shopify this would be things like homepage, collection, product, blogs and article pages.
- Define what schema.org types and properties you must add to each page of your Shopify website: homepage, product pages, collection pages, blog page, and article pages
There are differences for every eCommerce but the following are the specific types of pages and structured data we recommend.
Homepage
Organisation: Although it may seem insignificant, verifying your identity can make a significant difference. Machines like Google and Microsoft thrive on structured language and confirming information in their native tongue, which is why a simple confirmation can go a long way.
Website: Searching is important for eCommerce stores, this markup will describe to search engines how to do it.
Collections
BreadcrumbList: By applying schema markup to your website’s breadcrumb lists, you can assist Google in categorising the information and improve your search result’s quality.
FAQPage: FAQ schema is a type of schema markup that categorises content on “Frequently Asked Questions” pages as well as product and service pages that contain FAQs. This informs Google that the content is in a question-and-answer format.
Products
BreadcrumbList: (see above)
Product: Product schema markup is a form of structured data that defines the various components of your product pages to search crawlers. You can use it for services as well.
Offer: Describes an offer for a Product (typically prices, stock availability, etc).
AggregateRating: The star rating in Google search results is made possible by this schema markup type. Google utilises this data to create rich snippets that display brief descriptions under a website’s title and URL in search results.
Blog Posts
BreadcrumbList: (see above)
Article: By using Article Schema to mark up your posts and pages, search engines can accurately identify the headline, publication date, and primary image of your article. This information helps search engines determine how to showcase your content in search results, potentially resulting in greater visibility for your articles. As a result, your articles may be featured in various search features, providing greater exposure than standard search results.
Using a Shopify App for Schema
The implementation of Structured Data within Shopify requires a good knowledge of liquid files, HTML and more as well as great attention to detail. As such it can prove quite intimidating to the average store owner so why not let one of the many apps designed to improve your Shopify store look after this aspect for you.
Most of these apps provide a simplified dashboard where all you need to supply is relevant information for the different page types. The app will then do all the heavy lifting and coding for you.
Manual Schema Implementation for Shopify
If you are up for the challenge and have a good understanding of the Shopify liquid files then adding the schema to your store manually is an option and unlike an app less likely to affect your site speed.
The manual route starts with you navigating your CMS by heading to Themes > Actions > Edit Code and then from here you can start to add structured data to the relevant pages.
Schema Implementation Tips
- To ensure correct application of JSON-LD to a webpage, it is crucial to include curly brackets immediately following the closing <script> element. Additionally, curly brackets should be utilised whenever defining properties of a type within a type, similar to how Offer properties are defined in separate curly brackets. The information preceding and following this defines the main entity, or Product.
- Care must be taken with regard to cases and special characters. Quotes should not be used with schema.org markup, and it is case-sensitive, necessitating attention to detail.
- To ensure proper functionality of the markup, all required properties must be included. The specific properties required will vary based on the data type.
- Those seeking a comprehensive example of product page markup in JSON-LD can reference Google’s detailed documentation on product markup.
Testing your Schema
Both the Rich Results Test and the Schema Markup Validator are useful tools for testing structured data.
According to Google, it is best to begin with the Rich Results Test, which enables the generation of Google rich results for your pages. Next, the Schema Markup Validator can be used to test and validate all types of schema.org markup.
For further information, refer to the link provided to test your structured data.
International SEO
International SEO (Search Engine Optimization) refers to the process of optimising a website’s content and structure to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs) across multiple countries and languages.
The goal of international SEO is to ensure that a website is effectively targeting and reaching its intended international audience. This may involve strategies such as creating localised content for different countries or languages, implementing hreflang tags to indicate language and regional targeting, and ensuring that technical aspects of the website, such as URL structures and sitemaps, are optimised for international search engines.
Overall, international SEO is a crucial aspect of digital marketing for businesses looking to expand their reach and attract customers from around the world.
For those utilising the Shopify, Advanced Shopify, or Shopify Plus plans, it is possible to create region-specific or country-specific domains through the international domains feature. This feature generates sitemap files for all domains. With the exception of redirects to the primary domain, all domains are searchable by search engines.
Shopify ccTLDs, country subdomains, and country subfolders
Although Shopify supports international expansion, it is not fully optimised for SEO as it does not allow for country subfolders. As a result, there are two options for those looking to expand their business internationally:
- Create a country subdomain.
- Use a new domain or country TLD.
While Google maintains that there should be no difference in SEO benefits between subdomains and subfolders, this topic is still debated.
Hreflang
By default, Shopify lacks hreflang functionality, but you can add the code to the theme.liquid file to enable it. The code automatically generates URLs for different location subdomains/domains, and you can follow a guide to set it up.
Since many international Shopify stores are created by duplicating the original store, the URLs are in the original language. This can create issues if some products are only available in specific locations, as the hreflang tags will still generate for all alternatives, even if the product does not exist in those locations.
example.com/en/gb/example-product/ – exists as product
example.com/fr/fr/example-product/ – does not exist, still referenced in hreflang
example.com/de/de/example-product/ – does not exist, still referenced in hreflang
To address this, there are apps available that can assist with translating your website content and creating hreflang tags.
Building Links
Search engines utilise backlinks to assess the perceived value of your site within the broader community. It can be viewed as the SEO equivalent of word-of-mouth advertising, relying on off-page optimization to establish credibility and trustworthiness.
If you’re looking to obtain links for your store, here are a few useful tips:
- Supplier/Manufacturer Links: Established companies often allow authorised retailers to obtain links. Contact them to inquire about linking to your store.
- Industry/Influencer Voices: Reach out to industry leaders and influencers to generate interviews and content, which can result in links.
- Mentions: You may have mentions in several places without links. Utilise mention.com to identify these mentions and then reach out to request a link to your site.
- Broken Links: Conduct research to locate broken links for products and services similar to yours. Contact the site’s owner to request that they link to your site instead, providing mutual benefit by replacing the broken link while also providing you with a backlink. This strategy is particularly advantageous since broken links can harm SEO.
By using these techniques, you can enhance your store’s visibility and reputation, driving greater organic traffic and ultimately achieving more significant sales and success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimising your Shopify store for search engines is crucial for improving its visibility and attracting organic traffic. By implementing the various techniques and best practices discussed in this guide, such as optimising product pages, improving website speed, and building high-quality backlinks, you can boost your store’s search engine ranking and drive more qualified traffic to your site.
Remember, SEO is an ongoing process, and it’s essential to monitor and adjust your strategy continually. By using the various Shopify apps and tools available, you can simplify and streamline the optimisation process, ultimately, we hope leading to a successful and profitable online store.